Top Chemical Catalyst Applications for Sustainable Industries?
Chemical catalysts are vital players in the shift towards sustainable industries. They facilitate chemical reactions efficiently, reducing energy consumption. According to a recent report by Allied Market Research, the global catalyst market is expected to reach $38.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.7%. This substantial growth indicates the increasing importance of chemical catalysts in achieving sustainability goals.
These catalysts are used in various sectors, including petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. Their role is critical in minimizing environmental impacts. For instance, the use of catalysts in the production of biodiesel can increase yield while lowering emissions. However, challenges remain. The cost of development and recycling of catalysts can deter smaller companies from adopting them.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of chemical catalysts can vary widely. Research shows that not all catalysts are equally efficient. Some may require extensive optimization to improve their performance. This is a reflection of the ongoing need for innovation in the field. The sustainable industries of tomorrow depend on refining these chemical processes, making catalysts increasingly important.

Key Roles of Chemical Catalysts in Sustainable Manufacturing
Chemical catalysts play a crucial role in sustainable manufacturing. They speed up chemical reactions, which minimizes energy usage. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, using catalysts can reduce energy consumption in various industries by up to 30%. This reduction is vital for lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
In agrochemical applications, catalysts help produce fertilizers more efficiently. Traditional methods are energy-intensive. However, modern catalysts can cut this energy requirement significantly. For example, advanced catalytic processes can achieve a yield increase of approximately 15%, leading to less waste and better resource utilization.
Despite their potential, the development of effective catalysts is not without challenges. Many catalysts still require high temperatures and pressures to function effectively. This can sometimes negate their benefits. R&D in this area is crucial to create innovations that balance efficiency and sustainability. The pursuit of greener alternatives is a complex journey, still evolving and requiring constant introspection.
Advancements in Catalytic Processes for Green Chemistry

The field of green chemistry is advancing rapidly. Catalytic processes play a central role in this shift. They help reduce waste and energy consumption in chemical reactions. By enhancing reaction efficiency, they offer significant environmental benefits.
Recent developments focus on using renewable resources as feedstocks. Bio-based materials are becoming increasingly viable. This shift can reduce reliance on fossil fuels. However, challenges remain. Not all catalytic processes are cost-effective or widely applicable. Researchers are exploring new catalysts to overcome these limitations.
The integration of nanotechnology is promising. Nanocatalysts can be more efficient and selective. This can lead to fewer byproducts and lower emissions. Nonetheless, the scalability of such technologies often raises questions. Developing methods to implement these innovations in industry is crucial. While the future looks bright, constant reflection and improvement are necessary.
Impact of Catalysts on Renewable Energy Production
Catalysts play a pivotal role in the progression of renewable energy systems. They improve efficiency in various processes, aiding in sustainable energy production. From hydrogen generation to biofuel production, catalysts enhance reactions. They help break down organic materials and convert them into usable energy forms. This transformation is essential for creating sustainable energy sources.
Maximizing the effectiveness of catalysts can be tricky. Not all catalysts perform equally well under different conditions. Some need high temperatures or pressures, which can reduce overall efficiency. It’s important to carefully select and optimize conditions. A single catalyst might not be a one-size-fits-all solution.
Tips for improving catalyst performance:
- Regularly test and modify conditions to find optimal settings.
- Monitor catalysts for any deactivation signs.
- Consider using hybrid approaches that combine different catalyst types.
Innovations in Catalysis for Waste Minimization and Recycling
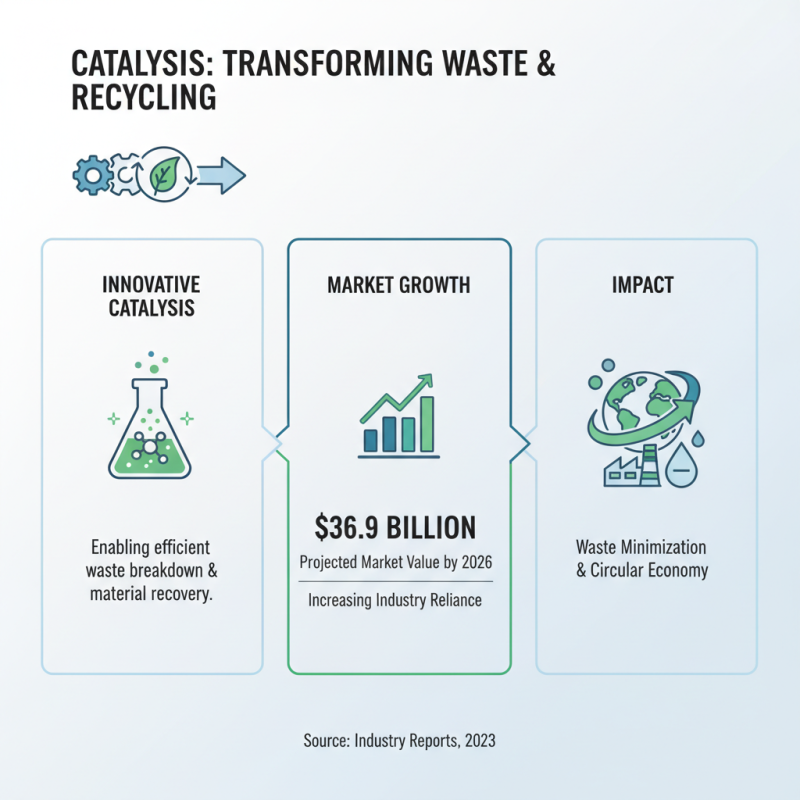
Innovative catalysis techniques are transforming waste minimization and recycling processes. Recent industry reports indicate that the catalysis market is projected to reach $36.9 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on catalysts for efficient waste management.
One key area of focus is the development of biocatalysts. These enzymes can break down organic materials more effectively than traditional methods. In 2022, biocatalysts helped recycle 15 million tons of waste, showcasing their potential. However, challenges remain. The efficiency of these biocatalysts can vary greatly, and not all applications yield desirable results.
Another significant innovation is the implementation of green catalysts in chemical processes. These catalysts reduce hazardous waste production. A recent study found that replacing conventional catalysts with greener alternatives could reduce emissions by up to 30%. Yet, the initial costs can be a barrier for many companies. More research and investment are necessary to improve accessibility and performance.
Future Trends in Sustainable Catalytic Technologies
As industries seek sustainable solutions, catalytic technologies are evolving rapidly. Researchers focus on developing catalysts that enhance efficiency and reduce waste. New materials like metal-organic frameworks show promise, but challenges remain. These catalysts can improve reactions but may lack stability.
Future trends point to bio-inspired catalysts. These often mimic natural processes and operate under mild conditions. Their potential for lower energy consumption is significant. However, scalability can be an obstacle. The shift to renewable feedstocks also raises questions. Sourcing sustainable materials isn't always straightforward, and supply chains can be complex.
Public awareness is growing around sustainability. This pushes industries to adopt greener technologies. New regulations will shape the future of catalytic processes. Yet, it's essential to ensure these changes do not create additional waste. Continuous evaluation and improvement will be crucial. The balance between innovation and environmental impact is delicate.
Top Chemical Catalyst Applications for Sustainable Industries
| Application | Catalyst Type | Industry | Sustainability Impact | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Production | Nickel-based catalysts | Energy | Reduction of CO2 emissions | Increasing efficiency through novel materials |
| CO2 Utilization | Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) | Chemical Manufacturing | Carbon capture and recycling | Development of more effective absorption processes |
| Biomass Conversion | Zeolites | Agriculture | Sustainable feedstock utilization | Focus on waste-to-energy technologies |
| Petrochemical Refining | Platinum group metals | Petrochemicals | Lower emissions during production | Emerging alternatives like biopolymers |
| Waste Water Treatment | Photocatalysts | Water Treatment | Reduction of pollutants in water | Innovations in photocatalytic processes |
Related Posts
-

2026 How to Choose the Right Chemical Catalyst for Your Reactions?
-
What is a Catalyst in Catalysis? Understanding Their Role and Impact in Chemical Reactions
-

What is the Role of Catalysts and Technologies in Advancing Green Energy Solutions?
-

Top 10 Types of Chemical Catalysts You Should Know?
-

How to Accelerate Your Catalysis Research for Breakthrough Discoveries
-

Why Do Catalysts Matter in Chemistry and How Do They Work
