Top 10 Catalytic Reactions You Should Know For Chemistry Success
In the realm of chemistry, understanding catalytic reactions is essential for students aiming for success in this intricate field. According to Dr. Emily Chen, a prominent expert in catalysis at the Green Chemistry Institute, "Catalytic reactions are pivotal in bridging fundamental chemistry concepts with real-world applications, making them key to sustainable development and innovation." This statement underscores the critical role that these reactions play not only in academic settings but also in addressing global challenges through efficient chemical processes.
This article aims to explore the top 10 catalytic reactions that every chemistry student should be familiar with. From fundamental mechanisms to practical applications, these reactions exemplify how catalysis can optimize chemical transformations and enhance reaction rates. By grasping these concepts, students can cultivate a deeper understanding of both the theoretical and practical aspects of chemistry, empowering them to contribute to advancements in the field.
As we delve into these essential catalytic reactions, it's important to recognize their impact on various industries, including pharmaceuticals, energy, and materials science. Understanding these processes can pave the way for innovative solutions and highlight the importance of catalysis in addressing pressing global issues.
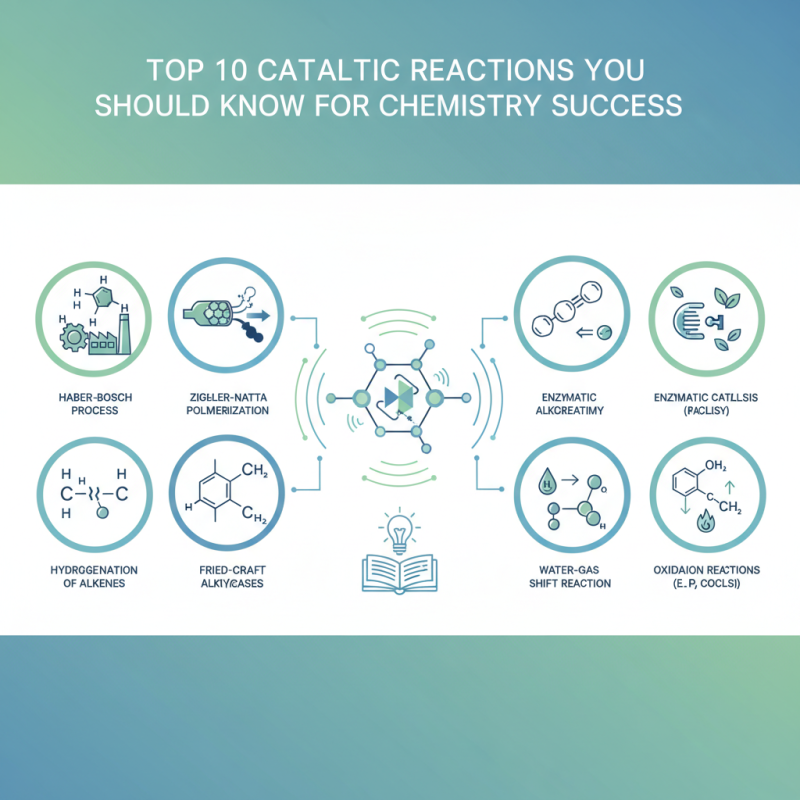
Key Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions in Chemistry
Catalytic reactions play a pivotal role in modern chemistry, characterized by their ability to increase reaction rates without being consumed in the process. These reactions are marked by their selectivity and efficiency, making them essential for various industrial applications.
According to the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), catalysts can enhance the efficiency of chemical reactions by a factor of up to 10,000, drastically reducing the energy required for processes like hydrocarbon reforming and synthetic fuel production.
Additionally, catalysts facilitate equilibrium shifts, allowing chemical reactions to reach greater yields faster. A study conducted by the American Chemical Society indicates that using catalytic processes in pharmaceuticals can lead to significant cost savings—potentially reducing production expenses by as much as 30%. This efficiency not only influences the economic viability of chemical production but also plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact by lowering waste generation and energy consumption.
Understanding these key characteristics of catalytic reactions is essential for chemists aiming to innovate and improve chemical processes in various fields, from energy production to materials science.
Types of Catalysts: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
Catalysts play a crucial role in enhancing the rate of chemical reactions without undergoing permanent changes themselves. They are primarily classified into two categories: homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. Homogeneous catalysts are present in the same phase as the reactants, typically in solution. This uniformity allows for greater interaction between the catalyst and the reactants, often leading to increased reaction efficiency. However, the challenge with homogeneous catalysis lies in the separation of the catalyst from the products after the reaction, which can complicate purification processes.
On the other hand, heterogeneous catalysts are in a different phase than the reactants, commonly solid catalysts acting on gaseous or liquid reactants. This phase difference facilitates easier separation of the catalyst from the products, making it a preferred choice in many industrial applications. Heterogeneous catalysis often involves solid surfaces where reactions occur, enabling larger reaction scales and continuous processes. Both types of catalysts serve essential roles in advancing chemical reactions, yet their unique characteristics determine their applications in various fields, from pharmaceuticals to environmental engineering.
Top 10 Catalytic Reactions You Should Know For Chemistry Success
Top Catalytic Reactions: Mechanisms and Applications
Catalytic reactions play a crucial role in the advancement of chemistry, facilitating a wide range of processes that are essential in both industrial and laboratory settings. Understanding the mechanisms behind these reactions allows chemists to harness their power efficiently. For instance, in many catalytic processes, the catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, leading to enhanced reaction rates. Common mechanisms include surface adsorption, where reactants bind to the catalyst's surface, and subsequent reaction steps that often involve the formation and breaking of chemical bonds. These steps are key to understanding how catalysts operate, influencing everything from reaction specificity to product yield.
Applications of catalytic reactions are vast and varied, spanning from the synthesis of pharmaceuticals to the production of fuels and materials. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, catalytic processes enable the efficient synthesis of complex molecules, reducing waste and maximizing yield. In environmental chemistry, catalytic converters in vehicles transform harmful emissions into less toxic substances, showcasing the importance of catalysis in promoting sustainability. Moreover, catalytic reactions contribute to innovations in green chemistry, where the focus is on developing methods that minimize environmental impact. Overall, understanding the mechanisms and diverse applications of catalytic reactions is essential for any chemist striving for success in the field.
Top 10 Catalytic Reactions You Should Know For Chemistry Success
| Reaction Name | Catalyst | Reaction Type | Applications | Mechanism Overview |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haber-Bosch Process | Iron Catalyst | Ammonia Synthesis | Fertilizers | N2 + H2 → NH3 under high pressure |
| Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis | Cobalt or Iron Catalyst | Hydrocarbon Production | Synthetic Fuels | CO + H2 → Long-chain hydrocarbons |
| Alkene Hydrogenation | Nickel Catalyst | Reduction | Food Industry (e.g., margarine) | Addition of H2 across double bonds |
| Wacker Process | Palladium Catalyst | Oxidation | Acetaldehyde Production | Alkene + O2 → Aldehyde product |
| Transesterification | Basic Catalyst (e.g., NaOH) | Exchange Reaction | Biodiesel Production | Triglycerides + alcohol → Esters |
| Grignard Reaction | Magnesium Catalyst | Nucleophilic Addition | Organic Synthesis | R-X + Mg → R-MgX |
| Diels-Alder Reaction | Lewis Acid Catalyst | Cycloaddition | Polymer Chemistry | Diene + Dienophile → Cyclohexene |
| Ethanol Dehydrogenation | Copper Catalyst | Dehydrogenation | Aldehyde Synthesis | C2H5OH → C2H4O + H2 |
| Bayer Process | Aluminum Hydroxide | Separation | Aluminum Production | Bauxite to Alumina |
| Catalytic Cracking | Zeolite Catalyst | Cracking | Petroleum Refining | Long-chain hydrocarbons to fuels |
Importance of Catalysis in Industrial Chemistry
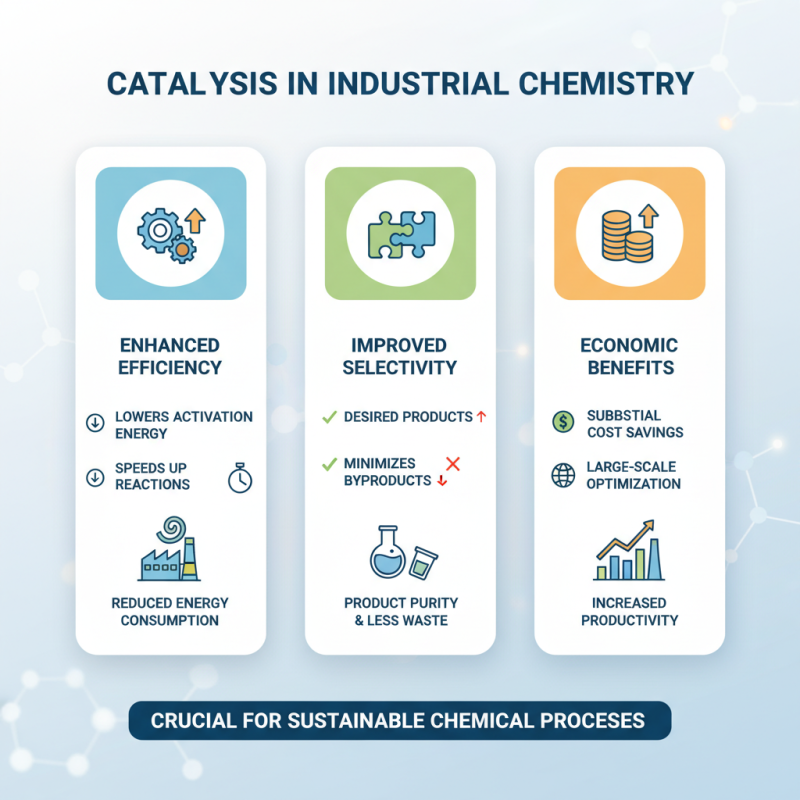
Catalysis plays a crucial role in industrial chemistry, significantly enhancing the efficiency and selectivity of chemical reactions. By using catalysts, industries can lower the activation energy required for reactions, thus speeding up the process and reducing energy consumption. This is particularly important in large-scale operations where even minor improvements in reaction rates can lead to substantial cost savings. Moreover, catalysts enable the production of desired products while minimizing unwanted by-products, which is essential for maintaining product purity and reducing waste.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of catalysis cannot be overstated. Catalytic processes are often designed to be more sustainable, resulting in less energy usage and lower greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with the global push towards greener chemistry, where the goal is to create processes that are not only economically viable but also environmentally friendly. As industries seek to meet stricter regulations and public demand for sustainable practices, the development and optimization of catalytic reactions will continue to be a focal point in advancing the field of chemistry. The importance of catalysis in industrial applications is therefore paramount, influencing not only economic factors but also contributing to sustainable development goals.
Factors Influencing Catalytic Activity and Selectivity
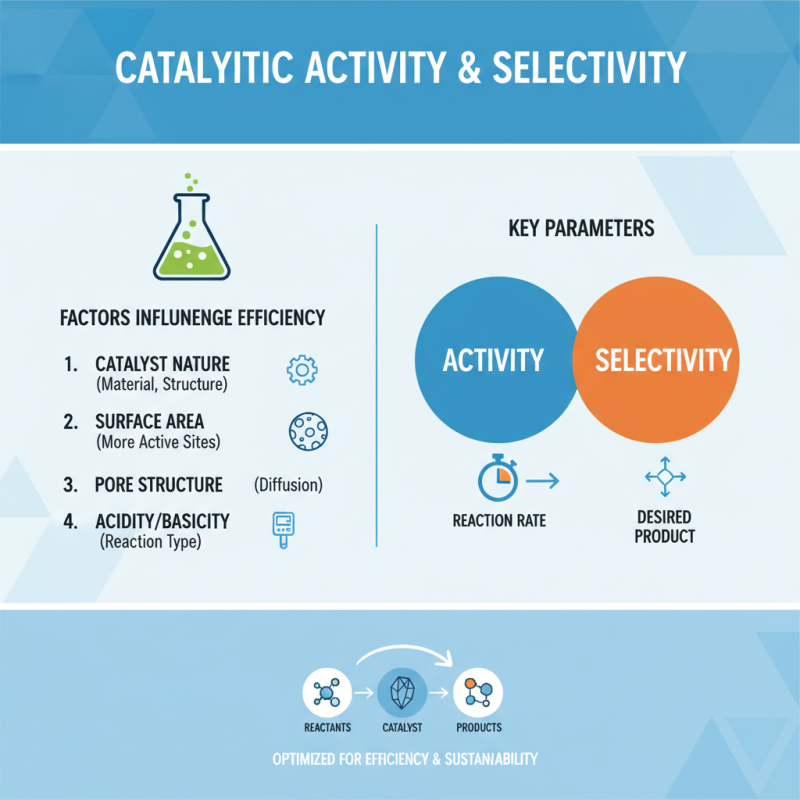
Catalytic activity and selectivity are critical parameters in determining the efficiency of catalytic reactions. Several factors influence these properties, starting with the nature of the catalyst itself. Catalysts can vary in their physical and chemical properties, affecting the rate at which they facilitate reactions. For instance, the surface area of a catalyst can play a significant role in its activity; a larger surface area means more active sites available for reaction, enhancing catalytic efficiency.
Temperature and pressure also significantly influence catalytic processes. Higher temperatures generally increase reaction rates, but they may also lead to unwanted side reactions. Conversely, optimizing pressure can enhance selectivity by favoring certain reaction pathways over others. Additionally, the presence of solvents and their properties can alter the interaction between reactants and the catalyst, further affecting both activity and selectivity.
Tip: When experimenting with catalytic reactions, consider systematically varying one factor at a time to pinpoint its effects on activity and selectivity. This methodical approach can yield valuable insights into optimizing your catalytic processes.
Another key consideration is the nature of the reactants themselves. The concentration and physical state of the reactants, as well as any potential inhibitors present, can significantly affect the overall catalytic performance. It’s essential to ensure the reactants are compatible and that the reaction conditions are meticulously controlled to achieve the desired outcomes.
Tip: Utilize kinetic studies to help identify the optimum conditions for your reactions, ensuring a balance between speed and selectivity. Understanding the kinetic profile can illuminate the best pathways for enhancing catalytic performance.
Related Posts
-
What is a Catalyst in Catalysis? Understanding Their Role and Impact in Chemical Reactions
-

How to Accelerate Your Catalysis Research for Breakthrough Discoveries
-

How to Leverage Catalyst Technologies for Business Growth and Innovation
-

What is the Role of Catalysts and Technologies in Advancing Green Energy Solutions?
-

Top Trends in Chemical Manufacturing for Sustainable Development
-

Top 10 Trends Transforming the Chemical Industry in 2023
