Top 10 Best Catalytic Reactions You Need to Know?
Catalytic reactions play a crucial role in modern chemistry. Renowned chemist Dr. Alice Thornton once stated, "Catalytic reactions transform simple compounds into complex products." This highlights their significance in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to energy. Understanding these reactions can unlock new possibilities.
In today's world, efficient catalytic reactions can lead to sustainable solutions. They help reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Yet, mastering these reactions is no easy task. The intricacies involved may sometimes lead to unexpected outcomes. Scientists continually strive to refine these processes, pointing to the evolving nature of chemistry.
Moreover, the selection of the right catalyst is vital. Missteps here can result in subpar yields. This underscores the importance of knowledge in choosing the best catalytic reactions. A deeper dive into this topic reveals the ten most essential catalytic reactions. They hold the potential to redefine our approach to chemical synthesis.

Overview of Catalytic Reactions in Chemistry
Catalytic reactions play a crucial role in modern chemistry. They enhance reaction rates and improve product yields. According to a report by the Catalysis Society, approximately 90% of all chemical processes involve catalysis. This statistic underscores the significance of catalysts in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and energy.
The mechanisms of catalytic reactions can be quite complex. Catalysts lower the activation energy of reactions, making them more efficient. However, not all catalysts are equally effective. A study from the International Journal of Chemical Engineering reveals that the efficiency of a catalyst can vary significantly based on its structure and the reaction conditions. For instance, certain catalysts may become inactive over time due to poisoning or deactivation.
In practice, finding the right catalyst is often a process of trial and error. Researchers frequently face challenges in optimizing conditions. Data indicates that more than 70% of catalytic experiments yield non-ideal results. These setbacks highlight the unpredictable nature of catalyst performance, and a deeper understanding is required to enhance efficiency and sustainability in catalytic processes.
Importance of Catalysts in Industrial Processes
Catalysts play a critical role in industrial processes. They increase reaction rates without being consumed. This efficiency often translates to significant cost savings. For instance, a report by the International Energy Agency states that catalysts are responsible for reducing energy consumption by up to 20% in several industries. This reduction not only cuts costs but also minimizes environmental impact.
In the production of chemicals, catalysts enhance selectivity and yield. Some estimates suggest that about 90% of chemical products are made using catalytic processes. However, not all catalysts are perfect. Some suffer from deactivation over time, which can lead to increased waste and inefficiency. Companies must constantly innovate to develop more robust catalysts that can withstand harsh conditions.
Catalysts also have a crucial economic impact. The global catalyst market was valued at approximately $30 billion in 2020, with projections showing steady growth. Surprisingly, many firms still underutilize this technology. This lack of awareness hinders potential gains. Therefore, enhancing knowledge about catalysts could revolutionize industrial applications, driving both sustainability and profitability.
Top 10 Catalytic Reactions and Their Applications
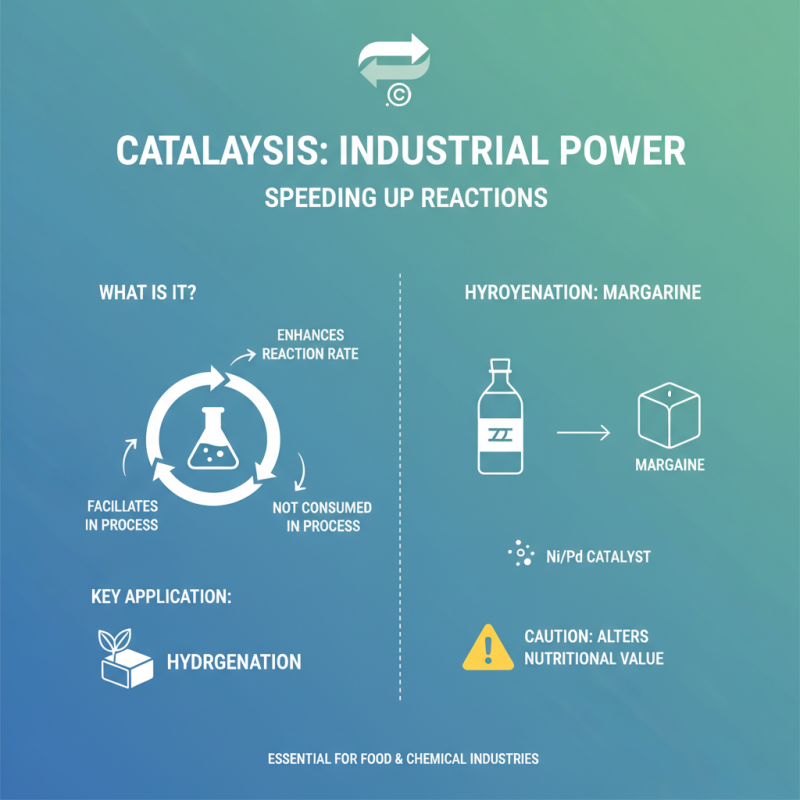
Catalytic reactions are vital in many industrial processes. They enhance reaction rates without being consumed themselves. One significant application is in hydrogenation, where unsaturated organic compounds are converted into saturated ones. For example, this reaction is crucial in the food industry to produce margarine from vegetable oils. However, it can alter the nutritional value, a point that requires careful consideration.
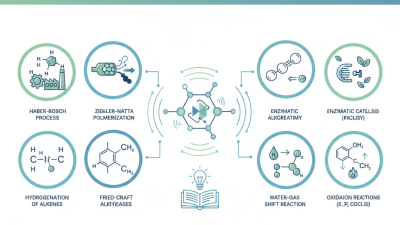
Another notable catalytic reaction is the Haber-Bosch process. This reaction synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gas. It's essential for fertilizer production, feeding millions. Despite its importance, the energy-intensive nature of this process raises environmental concerns. Moreover, the catalysts used can lose effectiveness over time, necessitating ongoing research for sustainable alternatives.
Catalysts also play a role in oxidation reactions, such as converting carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide. This process is vital for reducing emissions from vehicle exhaust systems. Yet, the effectiveness can fluctuate with different conditions. Minor impurities in the reactants can render the catalysts less efficient. Understanding these intricacies is key for future advancements in catalytic reactions and applications.
Mechanisms Behind Key Catalytic Reactions
Catalytic reactions are crucial in various fields, from industrial processes to biochemistry. They speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. Understanding the mechanisms behind these reactions is vital. For instance, enzyme catalysis involves the formation of a transient complex between the enzyme and the substrate. This complex stabilizes the transition state, making the reaction more efficient.
Another important reaction is heterogeneous catalysis. It occurs when the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants. The metal surface interacts with gas or liquid reactants, leading to product formation. This process can be complex. It involves adsorption, reaction, and desorption steps, all of which can be influenced by temperature and pressure.
Many reactions have multiple pathways. Each pathway may vary in speed and yield. It's not always clear why one pathway is favored over another. Scientists often revisit their assumptions. Observations can lead to new questions. Perhaps the most fascinating aspect of catalytic mechanisms is their unpredictability. A small change in conditions might alter the outcome significantly.
Top 10 Best Catalytic Reactions You Need to Know
| Reaction | Catalyst Type | Mechanism Type | Application | Reaction Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haber-Bosch Process | Iron Catalyst | Reductive Ammonia Synthesis | Fertilizer Production | High Temperature & Pressure |
| Friedel-Crafts Alkylation | Lewis Acid Catalyst | Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution | Organic Synthesis | Room Temperature |
| Contact Process | Vanadium Oxide Catalyst | Oxidation Reaction | Sulfuric Acid Production | High Temperature |
| Wacker Process | Platinum Catalyst | Oxidation | Ethylene to Acetaldehyde | Ambient Conditions |
| Hydroformylation | Rhodium or Cobalt Catalyst | Addition Reaction | Production of Aldehydes | Mild Temperature |
| Dehydrogenation | Nickel Catalyst | Elimination Reaction | Production of Olefins | High Temperature |
| Claus Process | Alumina or Titanium Dioxide | Rearrangement Reaction | Sulfur Recovery | Moderate Temperature |
| Nitration | Concentrated Nitric Acid | Electrophilic Substitution | Nitro Compound Production | Room Temperature |
| Bayer Process | Bauxite and Soda | Leaching Process | Alumina Production | High Pressure |
| Methanol Synthesis | Copper Catalyst | Hydrogenation Reaction | Fuel Production | High Temperature & Pressure |
Future Trends in Catalytic Reaction Development
Catalytic reaction development is evolving rapidly. Researchers are focusing on sustainability and efficiency. New materials and techniques are emerging. They promise to reshape industries. Renewable resources are becoming more common in these reactions. This shift is crucial for reducing environmental impact.
One notable trend is the use of machine learning. Algorithms help optimize reaction conditions. They analyze vast datasets quickly. This speeds up research significantly. However, these methods aren't flawless yet. Data quality and availability pose challenges. Finding reliable sources remains a task for scientists.
Another trend involves green chemistry. Catalysts that minimize waste are a key focus. Engineers seek to create more selective reactions. This often leads to fewer byproducts. Yet, balancing economic viability with environmental benefits is tricky. Some reactions are still too costly to implement widely. Researchers must continue exploring new pathways and approaches.
Top 10 Best Catalytic Reactions You Need to Know
This chart illustrates the popularity of various catalytic reactions based on their impact and application across different industries, showcasing the top 10 reactions that are critical for future trends in catalytic reaction development.
Related Posts
-

How to Accelerate Your Catalysis Research for Breakthrough Discoveries
-

What Are the 4 Types of Catalysts and Their Functions in Chemistry?
-
What is a Catalyst in Catalysis? Understanding Their Role and Impact in Chemical Reactions
-

What is the Role of Catalysts and Technologies in Advancing Green Energy Solutions?
-

How to Leverage Catalyst Technologies for Business Growth and Innovation
-
Top 10 Catalytic Reactions You Should Know For Chemistry Success
