Why Do Catalysts Matter in Chemistry and How Do They Work
In the realm of chemical sciences, the importance of catalysts cannot be overstated. These remarkable substances are pivotal in accelerating chemical reactions, making them a cornerstone of both research and industrial practices. Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in the field of catalysis, eloquently states, "Catalysts are not just facilitators of reactions; they are the unsung heroes that transform how we approach chemical processes." This highlights the fundamental role that chemistry catalysts play in enhancing efficiency and sustainability in chemical reactions.
Catalysts operate by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, thereby facilitating reactions that might otherwise proceed too slowly or require excessive energy input. Their ability to be used in small amounts while still exerting significant influence on reaction rates underscores their efficiency and utility in various applications, from pharmaceuticals to environmental chemistry. By understanding the mechanisms behind chemistry catalysts, scientists can innovate and design better catalysts that not only optimize reactions but also contribute to more sustainable practices in the industry. The exploration of catalysts continues to be a dynamic area of research, promising advancements that could lead to breakthroughs in multiple disciplines.

Importance of Catalysts in Chemical Reactions
Catalysts play a crucial role in chemical reactions by increasing the rate at which they occur without being consumed in the process. This is significant in both industrial and laboratory settings, where the efficiency of reactions can greatly impact productivity and cost-effectiveness. By lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed, catalysts allow reactions to occur at milder conditions, which can lead to safer and more economical processes. Their ability to facilitate reactions while remaining unchanged makes them invaluable in synthesizing complex molecules in pharmaceuticals, producing chemicals, and even in environmental applications like pollution control.
Moreover, the importance of catalysts extends beyond mere efficiency. They can influence the selectivity of reactions, guiding them toward desired products while minimizing unwanted by-products. This selectivity is particularly vital in multi-step synthesis, where a cascade of reactions must yield specific outcomes in a controlled manner. The use of catalysts enables chemists to tailor reactions to achieve higher yields of specific products, thus optimizing entire synthetic routes. In essence, their role is central to advancing chemical research and industrial practices, making catalytic processes essential for sustainable development and innovation.
Importance of Catalysts in Chemical Reactions
Mechanisms of Catalysis: How Catalysts Accelerate Reactions
Catalysts play a pivotal role in chemical reactions by significantly lowering the activation energy required for those reactions to occur. This reduction in energy allows reactions to proceed at a much faster rate, making catalysts vital in various industrial processes. According to a report from the American Chemical Society, the use of catalysts in chemical manufacturing can increase reaction rates by several orders of magnitude, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. This is especially important in large-scale chemical production, where even minor improvements can lead to substantial economic benefits.
The mechanisms of catalysis involve several key processes. One common mechanism is adsorption, where reactants bind to the surface of the catalyst, facilitating the formation of intermediates that are closer to the transition state of the reaction. This step can dramatically speed up the process compared to the same reaction occurring without a catalyst. Studies indicate that catalysts can also provide alternative reaction pathways, further accelerating the overall reaction rates. For example, metal catalysts in automotive exhaust systems are designed to convert harmful gases into less harmful substances, demonstrating the practical application of these mechanisms in environmental chemistry.
Tips: When working with catalysts, always consider the specificity of the catalyst to the reaction you are contemplating. Not all catalysts will work for every reaction, and choosing the right one can save both time and resources. Additionally, ensure proper handling and disposal of catalysts, as their effectiveness often diminishes after use, requiring careful management in laboratory and industrial settings.
Types of Catalysts: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Catalysis
Catalysts play a pivotal role in chemistry, enhancing the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They can primarily be classified into two categories: homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. Homogeneous catalysts exist in the same phase as the reactants, typically in a solution, allowing for uniform interaction and effective catalysis. This type of catalysis is often seen in organic reactions, where the catalyst can offer a unique mechanism that lowers the energy barrier, leading to reactions occurring at much lower temperatures. For instance, studies indicate that homogeneous catalysis can achieve efficiencies of up to 90% in specific reactions, making it highly valuable in synthetic organic chemistry.
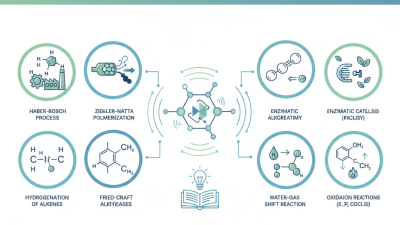
On the other hand, heterogeneous catalysts operate in a different phase than the reactants, often solid catalysts interacting with gaseous or liquid reactants. This type of catalysis is prevalent in industrial processes such as catalyzed combustion and the Haber process for ammonia synthesis. According to industry reports, the use of heterogeneous catalysts can increase reaction rates significantly while also simplifying the separation of products from the catalyst. The recent advancements have shown that improving the surface area and porosity of these solid catalysts can enhance reaction efficiency by a factor of 2-3 times, underscoring their importance in sustainable chemical production and energy conversion technologies. This duality of catalysts highlights their essential role in driving both fundamental and applied chemistry.
Real-World Applications of Catalysts: From Industry to Environment

Catalysts play a crucial role in various real-world applications, impacting industries from chemical manufacturing to environmental sustainability. In the chemical industry, catalysts are essential for increasing reaction rates and enhancing product yields, significantly reducing energy consumption and costs. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, the use of catalysts in industrial processes can save up to 15% of global energy use, underscoring their importance in driving efficiency. For instance, heterogeneous catalysts are extensively utilized in petrochemical refineries, where they facilitate reactions to convert crude oil into valuable products, optimizing output and minimizing waste.
Beyond the industrial sphere, catalysts are also pivotal in environmental applications. They are key in reducing harmful emissions from vehicles, with catalytic converters transforming toxic gases into less harmful substances, thereby improving air quality. A study published in the Journal of Environmental Science and Technology indicates that implementing advanced catalytic technologies in urban areas could reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by up to 50%, which is critical for meeting stricter environmental regulations. Furthermore, catalysts are being explored for sustainable processes, such as carbon capture and conversion, which not only mitigate greenhouse gas emissions but also generate usable fuels, emphasizing their transformative potential in overcoming environmental challenges.
Catalyst Efficiency: Measuring Activity and Selectivity in Reactions
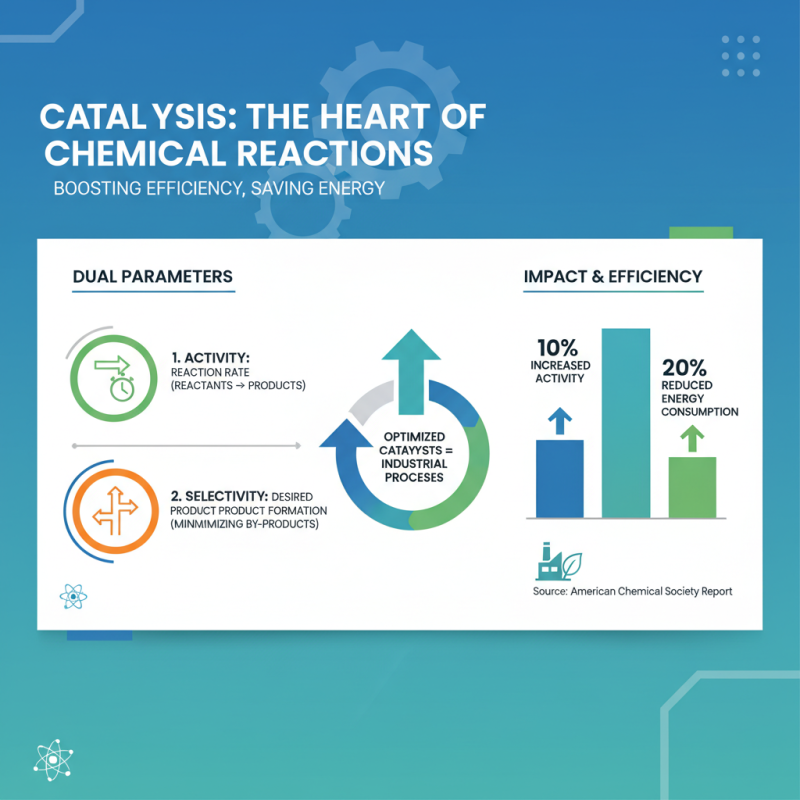
In the realm of chemistry, catalysts play a crucial role by enhancing the rate of chemical reactions without undergoing any permanent change themselves. Their efficiency can be measured through two primary parameters: activity and selectivity. Activity refers to the rate at which a catalyst converts reactants into products, while selectivity assesses how effectively a catalyst directs a reaction towards a desired product, minimizing the formation of by-products. Data indicates that optimizing both these parameters can significantly improve industrial processes. According to a report from the American Chemical Society, a 10% increase in catalyst activity can lead to a reduction in energy consumption by up to 20% in certain reactions.
Moreover, measuring catalyst selectivity is essential for increasing yield and reducing waste. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Catalysis highlights that catalysts with high selectivity can achieve conversion rates exceeding 90% for specific desired products, demonstrating their potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes. These improvements not only enhance the efficiency of chemical reactions but also contribute to more sustainable practices by lowering the environmental impact associated with excess by-products and energy use. As industries continue to seek greener alternatives, understanding and implementing effective catalysts becomes increasingly vital in advancing chemical engineering practices.
Related Posts
-
What is a Catalyst in Catalysis? Understanding Their Role and Impact in Chemical Reactions
-
Top 10 Catalytic Reactions You Should Know For Chemistry Success
-

How to Leverage Catalyst Services for Business Growth and Innovation in 2025
-

Top 10 Trends Transforming the Fine Chemical Industry in 2024: Insights and Data
-

How to Succeed in the Fine Chemical Industry and Boost Your Business Growth
-

How to Leverage Catalyst Technologies for Business Growth and Innovation
